[:en]Development of information technology has enabled us to process a huge quantity of language texts using a computer. However, fundamental information is not necessarily expressed in a text in a favorable fashion. Knowledge embedded into a text only becomes available through the understanding of its reader. Consequently, it is a great challenge for artificial intelligence to comprehend the fundamental function of human intelligence in which knowledge is transformed, combined, and used. We are conducting research on knowledge acquisition using language analysis by a computer and application of knowledge acquired, to undertake a more fundamental task: search for a widespread knowledge space generated by operations such as generalization, integration, and inference.
Combining fragmented knowledge: Text linking technology and its application
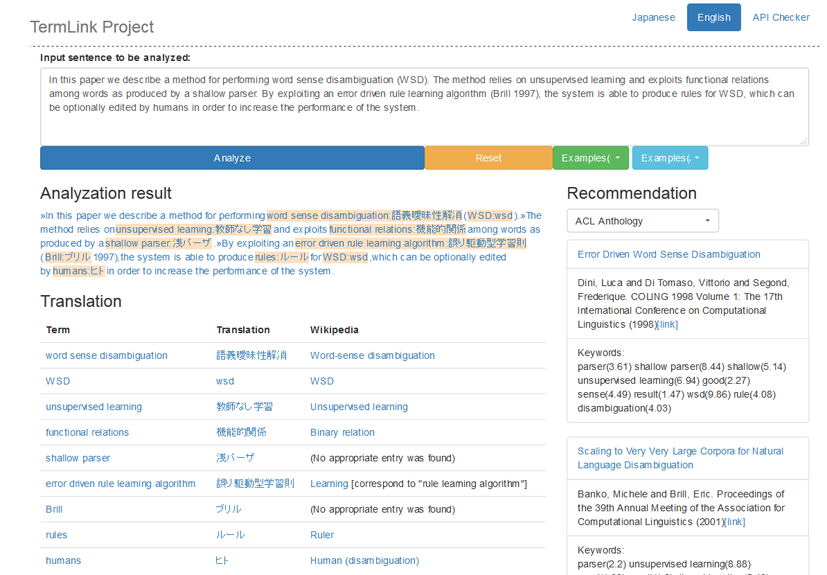
Knowledge processing by AI is demanded acutely in modern information societies to use a huge amount of contents produced and accumulated daily. Language processing technology, which carries out automated knowledge acquisition from a text, serves as the core. Especially “entity linking,” which connects the concept and identifier of things in a text to external knowledge, is attracting attention lately as an indispensable technology for knowledge acquisition. However, most present linking systems assume intrinsic expressions such as a person’s name, but they do not deal with abstract concepts that are useful for the systematization of knowledge. Accordingly, we specifically examine “technical terms” by which each domain is characterized, and study the regularization of terms, lexical resource compilation, term translation, and dissolution technology of equivocation for connecting a technical term to external knowledge sources. We have constructed a demonstration system as an example of knowledge processing by linking, which has a linking server for scientific documents and which performs reference recommendation from Japanese to English and extraction of links to related Wikipedia articles. Because concepts identified by linking constitute a base unit of information acquisition or knowledge inference, they are expected to be applied for discovery of knowledge across languages and domains and for the integration of knowledge bases.
Recommendation of relevant information adapted to the structure of a paper and the browsing support system
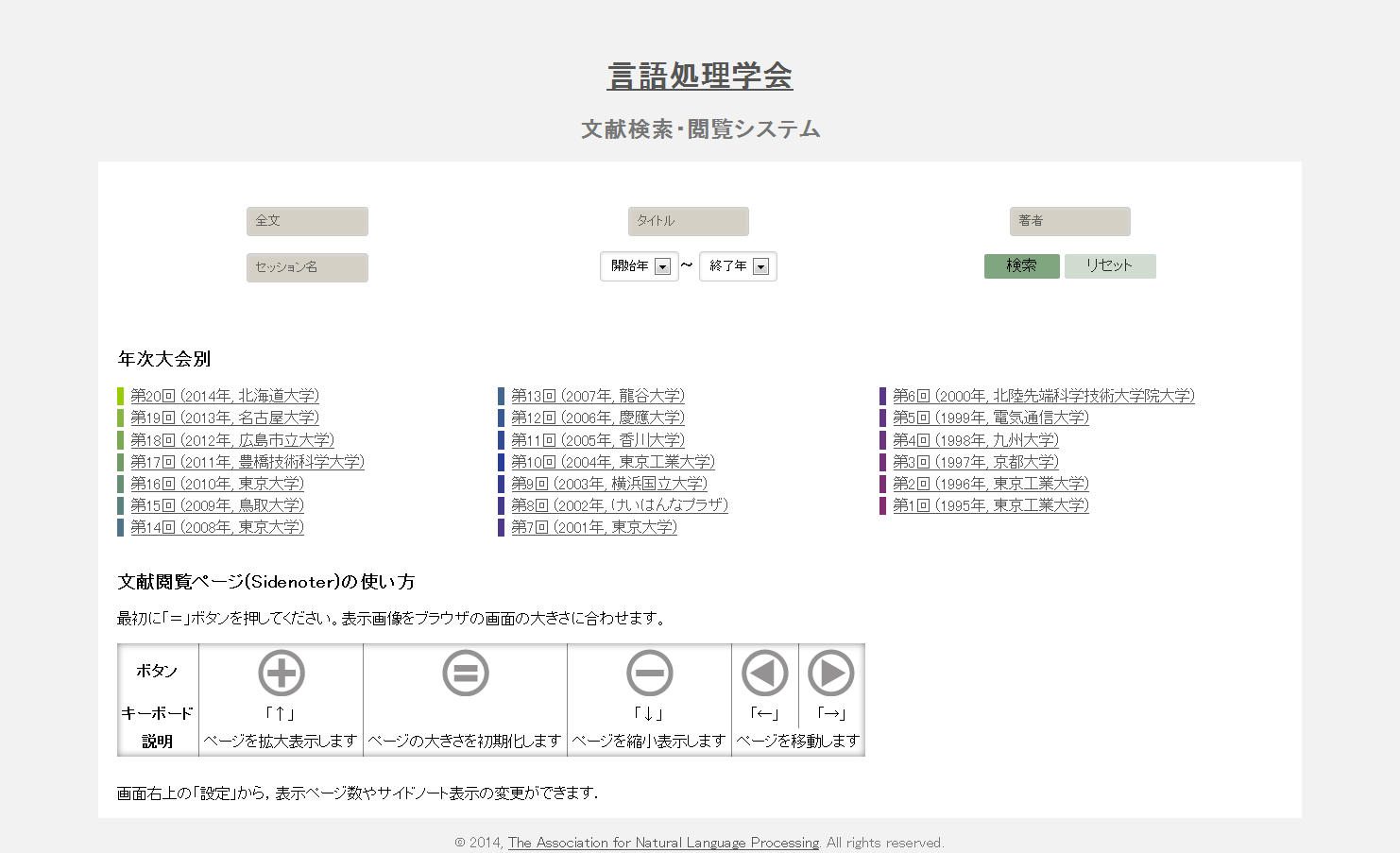
We study the information recommendation method, which presents useful relevant information and articles related to knowledge bases in accordance with logical structures such as sections and paragraphs of a document. We are also developing and operating SideNoter, a PDF browsing system with annotations for scientific papers in cooperation with Dr. Takeshi Abekawa of NII. SideNoter displays recommendation information automatically by the side of a page as an annotation. We operate a demonstration site using the Archive of Proceedings for NLP Annual Meeting that is currently open to public by the Association for Natural Language Processing of Japan. Implementation of SideNoter requires diverse technologies such as the structure analyses of PDF documents, term linking, identification of references, and multilanguage paper recommendation so that the application of SideNoter is anticipated as the demonstration base of the logical, semantic, and structural analytic method of papers containing these. (Collaborators: Takeshi Abekawa and Takeshi Sagara)
Extraction of natural language sentences from structurized documents
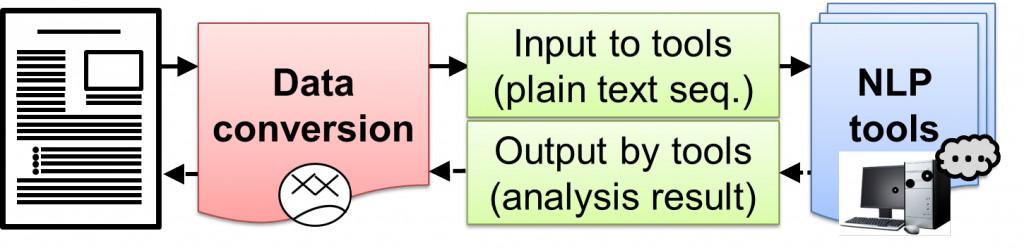
Most natural language processing tools premise a “sentence” as an input. However, many actual documents as analytical objects carry various structural information embedded in the text, such as a title and notes, so that existing natural language tools are inapplicable. We propose a framework for supporting an objective to “analyze documents of the real world containing structurized texts with natural language processing (NLP) tools in hand” in this project, and mounted a converting tool PlaneText. Its latest version can convert an XML-tagged text to a sentence that is directly accepted by an NLP tool. This approach not only enhances the quality of a “sentence” extracted from a document but improves the efficiency of syntactic analysis. (Tadayoshi Hara and Goran Topić)
Paper recommendation in which relevant papers are presented from diverse viewpoints
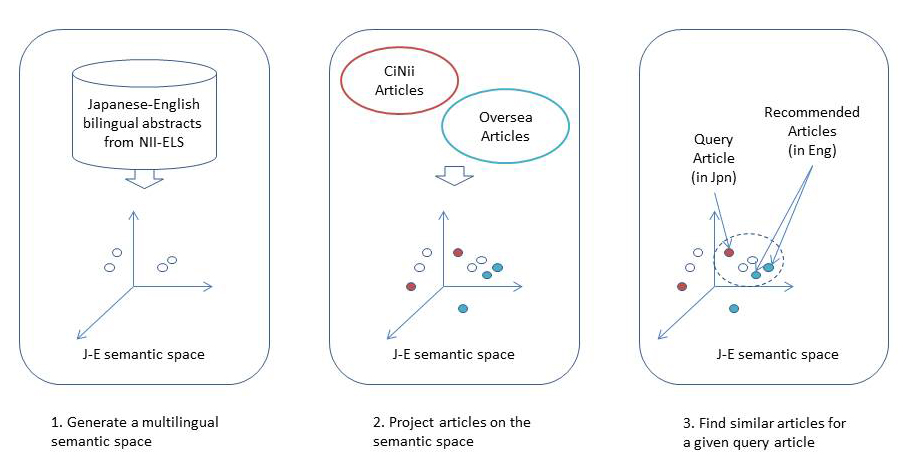
We constructed a recommendation system that enables us to conduct a paper search based on diverse viewpoints such as “popularity degree” or “discipline dissimilarity.” Relevant papers to the given paper are nominated. Then they are graded based on various viewpoints by multiple recommenders. Finally they are presented to the user in this system. We have mounted many advanced features as follows experimentally: (1) personalization feature to extract keywords from papers of the user’s own in the past, and to recommend papers of high relevance using them preferentially; (2) multilanguage recommendation feature to recommend the latest papers of domestic and overseas from the search results of Japanese papers; (3) semantics and role assignment feature to classify technical terms used in a paper and present them whether they are the objective or the means of the paper; and (4) serendipity recommendation feature to compute the distance between disciplines and to assign priority to papers with high unpredictability. Although the project was completed in 2012, the experience has been inherited to the succeeding project. (Collaborators: Atsuhiro Takasu, Kiyoko Uchiyama, Hidetsugu Namba, and Takeshi Sagara)
Academic linkage: Data integration by identification of scientific articles and researchers
We have studied a high-speed information linkage technology for associating bibliographic information related to scientific paper databases or book catalogs, and quoted strings extracted from whole papers or websites, and have developed a high-speed bibliographic identification engine i-linkage using suffix arrays and machine learning. We have constructed a researcher identification system that identifies the names of tens of millions of paper authors using this bibliographic identification. This method is a core technology that is indispensable to the advancement of the scholarly information infrastructure. Its importance is broadly recognized. The engine developed in this study has been used for the identification of papers and authors in NII service or in the succeeding project.[:ja]情報技術の発達によって、膨大な量の言語テキストを計算機で扱うことが可能になりました。しかし、必要な情報が、必要とするそのままの形でテキスト中に書かれているとは限りません。テキスト中に埋め込まれた知識は、それを読む人間の理解を介して、はじめて知識として利用可能な形になります。このように知識を変換したり組み合わせたりして活用する人間の知能の本質的な働きを捉えらることは、人工知能の大きなチャレンジとなっています。本プロジェクトでは、汎化や統合、推論などの操作により生み出される広がりを持つ知識空間の探索という、より本質的な課題に挑戦するため、計算機による言語解析を用いた知識の獲得、および、獲得した知識の活用に関する研究を進めています。
断片化する知識をつなぐ:テキストのリンキング技術とその応用

情報社会において日々生産・蓄積される膨大な量のコンテンツを活用するために、AIによる知識処理が切実に求められています。文章から知識を自動獲得する言語処理技術はその中核となるもので、中でも文章中の概念や事物の名前を外部知識に結びつける「エンティティ・リンキング」は、知識獲得に必須の技術として近年注目を集めています。しかし、現在のリンキング・システムの大半は人物名などの固有表現を想定するもので、知識の体系化に役立つ抽象的な概念は対象となっていません。そこで本プロジェクトでは、個々のドメインを特徴付ける「専門用語」に焦点をあて、専門用語を外部知識源に結びつけるための用語正規化、辞書構築、用語翻訳、語義あいまい性解消技術の研究を進めています。本研究ではリンキングによる知識処理の一例として、科学技術文書を対象とするリンキングサーバを実装するとともに、それを利用して日本語から英語への文献推薦やウィキペディア記事へのリンク抽出を行うデモシステムを構築しています。リンキングにより同定された概念は、情報獲得や知識推論の基本単位となることから、言語や分野を横断する知識発見や知識ベースどうしの統合などへの応用が期待されます。
論文の構造に沿った関連情報の推薦と閲覧支援システム

文書のセクションや段落などの論理構造に沿って、参考になる関連情報や知識ベース上の記事を推薦する文書閲覧支援の研究に取り組んでいます。特に、論文を対象とする「注釈付きPDF閲覧システムSideNoter」の開発・運用を、NIIの阿辺川武氏と協力して進めています。SideNoterは、推薦情報を注釈としてページの横に自動表示するもので、現在は、言語処理学会が公開している言語処理学会年次大会予稿集アーカイブを使ったデモサイトを立ち上げています。SideNoterの実現には、PDF文書の構造解析、用語リンキング、引用文献の同定、言語横断論文推薦など多様な技術が必要で、これらを含む論文の論理・意味構造解析手法の実証基盤としてSideNoterの活用が期待されます。(共同研究者:阿辺川武、相良毅)
構造化された文書からの自然言語文の抽出

自然言語処理を行うためのツールは、その入力として「文」を前提とするものが殆どですが、実際に解析対象となる文書の多くには、見出しや注釈など様々な構造情報がテキスト中に埋め込まれていて、そのままでは既存の自然言語ツールを適用することができません。本プロジェクトでは、「構造化されたテキストを含む実世界の文書を、手持ちの自然言語処理 (NLP) ツールで解析したい」という目的を支援するための枠組を提案し、PlaneTextと呼ぶ変換ツールを実装しました。現在のバージョンでは、XML タグで囲まれたテキストを NLP ツールに直接入力できるような文に変換することができます。このような取り組みによって、文書から抽出される「文」の質が高くなるとともに、構文解析等の効率も高めることができます。(原忠義、Goran Topić)
多様な観点から関連論文を推薦するオススメ論文推薦

本研究では、「人気度」「異分野性」などの多様な視点による論文検索を可能にする推薦システムを構築しました。このシステムでは、与えらえた論文に関連する論文を、複数のレコメンダが異なる視点に基づきランキングして利用者に提示します。(1)利用者が過去に執筆した論文からキーワードを抽出して、それを利用して関連の高い論文を優先的に推薦するパーソナライズ機能、(2)日本語論文の検索結果から国内・海外の最新論文を推薦する言語横断推薦機能、(3)論文中で使われている専門用語について論文の目的であるか手段であるかを分類して提示する意味役割付与機能、(4)分野間の距離を計算して意外性の高い論文を優先するセレンディピティ推薦など、多くの先進的な機能を試行的に実装しました。プロジェクトは2012年に終了しましたが、その経験は継続プロジェクトに引き継がれています。(共同研究者:高須淳宏、内山清子、難波英嗣、相良毅)
アカデミックリンケージ:書誌・著者同定によるデータ統合

論文データベースや図書カタログ上の書誌情報と、論文本文やウェブから抽出される引用文字列とを対応付けるための高速な情報リンケージ技術の開発に取り組み、サフィックスアレイと機械学習を用いた高速な書誌同定エンジン i-linkageを開発しました。また書誌同定を利用して、数千万人規模の論文著者を名寄せする研究者同定システムを開発しました。このような手法は学術情報基盤の高度化に欠かすことができないコア技術で、その重要性は広く認識されています。開発したエンジンは現在も、NIIサービスや後継プロジェクトでの論文や著者の同定に活用されています。[:]