[:en]Language activities through the screen of an electronic terminal are indispensable to our everyday life. We specifically investigate a human act of “reading” on a screen and performing research on its measurement, modeling, and support in this project. Specifically, we regard an act of “reading” a text on a screen as the interaction of the following three factors: (1) semantic structure of an object text; (2) image features, such as a layout and character decoration; and (3) a reader’s visual sense and language cognitive process. Our goal is to develop a method for presenting a text in a readable form, as well as studying the measurement and modeling method.
Text-gaze alignment using language model
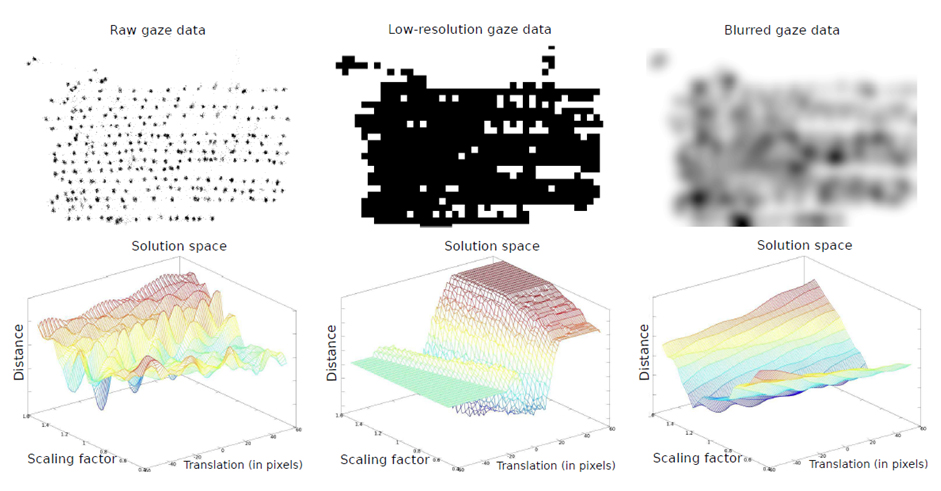
The analysis of “reading” requires extracting a “word” to which a reader is attentive each time. It is nevertheless difficult in actual conditions to realize sufficient accuracy for analysis in an ordinary gaze measuring environment. Accordingly, we study a method with enhanced accuracy in associating of a gaze and a text by introducing a language model and a cognitive model in this project. Progress in IT technology has diversified objects for reading and has also complicated the skill of reading. It is expected that improved measurement accuracy of reading will facilitate log collection in a natural environment, which can then contribute to research of a reading model. (Akito Yamaya, Goran Topić, and Pascual Martinez-Gomez)
Modeling of gaze prediction based on linguistic analysis and text structure
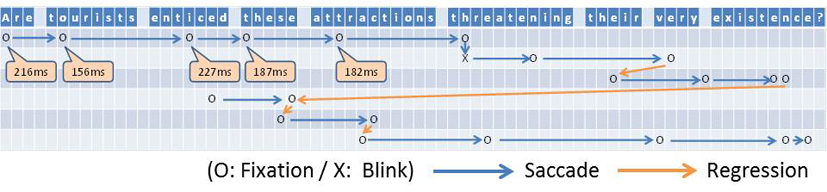
The appearance and contents of a text have inseparable relation in the act of “reading.” However, text segmentation and reader attributes have been investigated independently of the language processing of a text in many cases. We accordingly investigate methods for analysis and prediction of movement of a gaze recorded using a gaze measuring device, with comparison to (1) the structure and semantics of a text; (2) image features; and (3) reader attributes. Conventional natural language processing addresses “what is written,” whereas “what is read” has been treated as a subject in cognitive psychology or brain science. The language processing of “the way of being read,” particularly addressing the image feature of a document and the reader’s situation is a novel approach. It is presumed to induce broad application including support for reading and writing of on-line information. (Pascual Martinez-Gomez, and Tadayoshi Hara)
Document layout optimization based on semantic analysis of contents
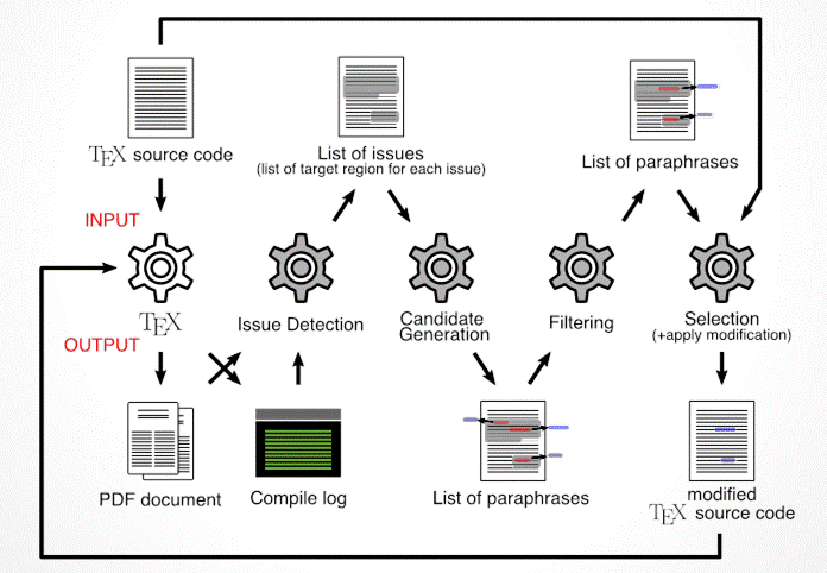
Positioning of document constituents is devised considering the continuity of regions and beautiful printing in document layout optimization by a computer. Usually, neither the text contents nor the text itself are examined or rewritten. We have developed a method of optimizing a document layout more flexibly by closely positioning a chart and a text that mentions it or adjusting the text segment size by paraphrasing. (Yusuke Kido and Kyohei Tomita)[:ja]電子端末の画面を介した言語活動は、我々の日常生活になくてはならないものとなっています。本プロジェクトでは、画面上で人がテキストを「読む」という行為に焦点をあてて、その計測・モデル化・支援についての研究を行っています。具体的には、画面上でテキストを「読む」行為を、(1)対象テキストの意味構造、(2)レイアウトや文字飾りなどの画像特徴、(3)読み手の視覚・言語認知プロセス、の三者インタラクションと捉えて、その計測およびモデル化手法を研究するとともに、読みやすい形でテキストを提示するための手法の開発にも取り組んでいます。
言語モデルを用いた視線とテキストのアラインメント技術

「読み方」の分析では、各時点で読み手が注視している「語」を抽出することが必要となりますが、通常の視線計測環境では、分析に必要な精度を実現することが難しいのが実情です。そこで本プロジェクトでは、言語モデルや認知モデルを導入することで、視線とテキストの対応付けの精度を高める手法の研究を行っています。IT技術の進歩によって読むべき対象が多様化して読み方のスキルも複雑になる中で、読みの計測精度が高まれば、自然な環境におけるログの収集が容易になり、読み方モデルの研究に役立つことが期待されます。(山谷彬人、Goran Topić、Pascual Martínez-Gómez)
言語解析と文書構造に基づく視線予測モデルの作成

「読む」という行為において、テキストの外見と内容は切り離せない関係にあります。しかし、テキストセグメントの配置や読み手の属性は、多くの場合、テキストの言語処理とは独立に研究されています。そこで本研究では、視線計測装置を用いて記録した視線の動きを、(1)テキストの構造や意味、(2)画像特徴、(3)読み手の属性、と照合しながら分析・予測する手法を検討しています。従来の自然言語処理は「何が書かれているか」を研究対象としており、「何が読まれるか」については、認知心理学や脳科学の課題として扱われてきました。これに対して、文書の画像特徴や読み手の状況に注目した「読まれ方」の言語処理は新しい取り組みで、オンライン情報の読み・書きの支援を含む幅広い応用にも結び付くと考えられます。(Pascual Martínez-Gómez、原忠義)
コンテンツの意味解析に基づく文書最適化

コンピュータによる文書レイアウトの最適化では、領域の連続性や印刷の美しさなどを考慮して、文書構成要素の配置を工夫します。通常は、テキストの内容が考慮されたり、テキスト自体が書き換えられることはありません。これに対して本研究では、図表とそれらに言及しているテキストを近くに配置したり、言い換え技術を適用してテキスト・セグメントのサイズを調整したりすることで、より柔軟に文書レイアウトを最適化する手法を開発しています。(城戸祐亮、冨田恭平)[:]